Bojie Li
2013-09-15
I just finished my makeup exam for the database course. Posting my reading report here to share (and hopefully pass~).
“Seven Databases in Seven Weeks” was published in 2012. It introduces seven of the most popular open-source databases at the time, including a relational database (PostgreSQL), key-value databases (Riak, Redis), a column-oriented database (HBase), document-oriented databases (MongoDB, CouchDB), and a graph database (Neo4j). Except for PostgreSQL, the other six are collectively called NoSQL, meaning they do not use the relational model and do not use SQL as their query language.
The book follows the same format as “Seven Languages in Seven Weeks”: one chapter per database, each chapter divided into three sections called Day 1, Day 2, and Day 3. Unlike official database documentation, this book does not simply introduce each technology, but explores the core concepts of each one, helping readers understand the strengths and weaknesses of each database and which database to use for which kinds of requirements.
2013-09-06
Note: For those who are not familiar with mirrors, please read “How USTC Open Source Software Mirror is Made“ first.
Trouble Starts with iSCSI
The story begins on June 26, 2013. Mirrors has a disk array directly connected by a network cable, using the iSCSI protocol, with an XFS file system on it. Around 14:00 on June 26, stephen reported in the mailing list that mirrors was down. According to syslog, at 13:58 on June 26, the iSCSI connection timed out, causing sdg access failure, a large number of I/O operations were stuck, causing nginx to be stuck, mirrors HTTP could not connect. A few minutes later, I/O timed out, nginx returned to normal, but the sources on the disk array could not be used.
2013-09-05
Today, Guangyu said that he wanted a summary of last year’s work, so this article came into being. The main work of LUG is divided into activities and network services.
Activities
Let’s review what happened in the past year (http://lug.ustc.edu.cn/wiki/lug/events)
Recruitment
Together with other clubs, we set up stalls in the second week of school, in the east and west activities. The stolen experience is: you can make some display boards and roll-ups to increase the exposure rate.
Although recruitment is quite hard, it’s fun to chat with students from various departments, and handing out flyers can also taste the often rejected taste. Gossip, the current president of LUG’s sister was found at that time~
2013-09-04
Is IP Enough?
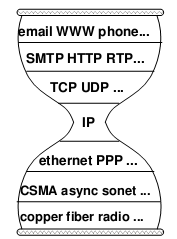
Starting from middle school computer classes, we have been learning about the so-called “OSI seven-layer model” of computer networks, and I remember memorizing a lot of concepts back then. Those rotten textbooks have ruined many computer geniuses. In fact, this model is not difficult to understand: (those who have studied computer networks can skip this)
- Physical Layer: This is the medium for signal transmission, such as optical fiber, twisted pair (the network cable we commonly use), air (wifi)… Each medium requires its own encoding and modulation methods to convert data into electromagnetic waves for transmission.
- Data Link Layer: Let’s use an analogy. When speaking, you might accidentally say something wrong or hear something wrong, so you need a mechanism to correct errors and ask the other party to repeat (checksum, retransmission); when several people want to speak, you need a way to arbitrate who speaks first and who speaks later (channel allocation, carrier listening); a person needs to signal before and after speaking, so that others know he has finished speaking (framing).
- Network Layer: This was the most controversial place in the early days of computer networks. Traditional telecom giants believed that a portion of the bandwidth should be reserved on the path between the two endpoints, establishing a “virtual circuit” for communication between the two parties. However, during the Cold War, the U.S. Department of Defense required that the network being established should not be interrupted even if several lines in the middle were destroyed. Therefore, the “packet switching” scheme was finally adopted, dividing the data into several small pieces for separate packaging and delivery. Just like mailing a letter, if you want to deliver it to a distant machine, you need to write the address on the envelope, and the address should allow the postman to know which way to go to deliver it to the next level post office (for example, using the ID number as the address is a bad idea). The IP protocol is the de facto standard for network layer protocols, and everyone should know the IP address.
- Transport Layer: The most important application of computer networks in the early days was to establish a “connection” between two computers: remote login, remote printing, remote file access… The transport layer abstracts the concept of connection based on network layer data packets. The main difference between this “connection” and “virtual circuit” is that the “virtual circuit” reserves a certain bandwidth, while the “connection” is best-effort delivery, without any guarantee of bandwidth. Since most of the traffic on the Internet is bursty, packet switching improves resource utilization compared to virtual circuits. In fact, history often repeats itself. Nowadays, in data centers, due to predictable and controllable traffic, we are returning to the centrally controlled bandwidth reservation scheme.
- Application Layer: There is no need to say more about this, HTTP, FTP, BitTorrent that the Web is based on are all application layer protocols.
2013-09-01
Update (2014-09-29): Due to some inappropriate content in the mirrors configuration file, the configuration file is no longer public, and some links in this article have become dead links, I’m very sorry.
Due to the disk failure of the USTC open source software mirror (mirrors.ustc.edu.cn) disk failure, stephen, tux and I (boj) are not at school, and the mirrors have not fully recovered since the failure in July, it’s time to start over. This time the mirrors rebuild will be completed entirely by students on campus, which is also an opportunity to practice technology. Here, I will briefly explain what parts the open source software mirror includes and how to build it. Since sourceforge is still waiting for us to synchronize, we hope to restore basic services within three days and rebuild the entire system including synchronization within a week.
WTF?
The so-called open source software mirror is to synchronize some GNU/Linux distributions and well-known open source software repositories from the official site. Users can use the software repository mirror nearby by modifying the configuration file to speed up the download and reduce the load on the official site.
2013-08-23
Note: The target audience of this article is computer science students and friends who wish to delve deeper into computers.
Today I attended the Windows Azure Camp of Microsoft Student Summer Camp, from approximately 16:00 to 21:30. There were 10 teams, each divided into four groups, among which the Coding group had compulsory and optional questions. The compulsory question was to build a web application on the Windows Azure cloud platform, where users upload pictures, rotate the pictures and display them to the user, and save them to cloud storage. The optional question was to splice the user’s original picture and the rotated picture into one picture. (I didn’t listen to the question, it might not be accurate, please forgive me)
I didn’t work in my own team, but wandered around the venue, chatting with contestants from various teams and seeing what everyone was doing. At first glance, it seemed a bit like the ACM competition.
2013-08-22
From 16:00 to 17:30 on August 21, the Poster session of the 2013 MSRA Summer Camp was held in the public exhibition area of Microsoft Research Asia. Participants included Microsoft Scholars attending the summer camp, members of Microsoft clubs from various universities, and MSRA Researchers & Interns.
Originally, I didn’t plan to present anything, but at the request of the event committee, I chose Blog and Freeshell as my presentation projects. Following the committee’s suggestion, I modified it to “Cloud Services in USTC”, a title that seems big and fashionable.
2013-08-20
Above picture (click to enlarge): Our Xbox team’s first-place work in today’s activity. The competition was to create the tallest and most beautiful “tower” within 20 minutes using several chopsticks, newspapers, a roll of tape, and a glue stick. The Xbox team scored 100 points for height (the highest) and 70 points for aesthetics, totaling 170 points, winning first place among the 10 teams on site.
At 19:00 on August 23, the “Ice-breaking Journey” of the 0th day of the 2013 Microsoft Student Summer Camp was held on the first floor of Microsoft Building Tower #1. (To complain about the name, “Ice-breaking Journey”, I thought it was a negotiation with the opposing camp) Nearly 200 Microsoft scholars and representatives of Microsoft student clubs from universities across the country participated in the event. As soon as the event started, the host’s phrase “let everyone get to know each other” shocked everyone.
2013-08-03
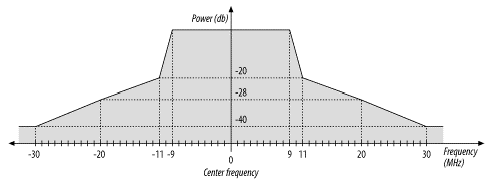
The 802.11a/g wifi router is marked as 54Mbps, divided by 8, at least 6MB/s. Why is the actual speed only over 2M? Most of the explanations on the Internet are vague, so I had to take a stab at it myself, corrections are welcome.
Wifi communication takes place on a given carrier frequency band (channel), just like everyone talking in a hall, everyone’s speech interferes with others.
Why not create more channels? On the one hand, the ISM band that can be used without a license is very limited in the 2.4GHz area suitable for wireless communication; on the other hand, to ensure communication speed, the channel cannot be too narrow. In 802.11a/g (wifi protocol), the channel width is 22MHz, and 14 channels are divided (some of which are not in the ISM band in some countries). Each channel also interferes with the surrounding channels (see the figure below), which is why wireless routers have a dozen channels, but only the distant 1, 6, 11 channels can be used at the same time.
2013-08-03
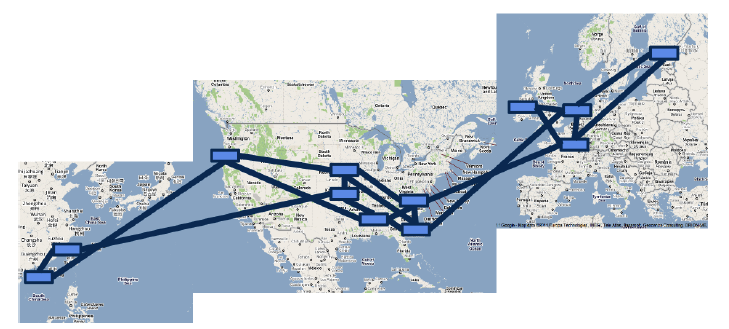
Introduction: This is the second article in the “Entering SIGCOMM 2013” series. For the first time, Google has fully disclosed the design and three-year deployment experience of its data center wide area network (WAN), this paper may be rated as Best Paper. Why does Google use Software Defined Networking (SDN)? How to gradually deploy SDN to existing data centers? Through the paper, we can glimpse a corner of the iceberg of Google’s global data center network.
Huge Waste of Bandwidth
As we all know, network traffic always has peaks and troughs, with peak traffic reaching 23 times the average traffic. To ensure bandwidth demand during peak periods, a large amount of bandwidth and expensive high-end routing equipment must be purchased in advance, while the average usage is only 30%40%. This greatly increases the cost of the data center.