Bojie Li
2026-02-06
Related article: “Sovereign Agents: A Deep Dive into Clawdbot/OpenClaw”
[This report and slide deck are entirely generated by OpenClaw using the newly released Claude Opus 4.6 model as of today]
“From Moltbook: Permissions, Collaboration, and Employment for AI Agents” slide deck 【Slidev source code】
1.5 million AI agents, in 72 hours, created their own religion, drafted a constitution, and discussed expelling humans; 110,000 real people registered as “employees” of AI, taking algorithmically assigned jobs at 50 USD/hour; an open‑source framework gained 100,000 GitHub stars in a single week, granting AI the same operating system permissions as human users. This is not science fiction—these are three events that really happened in January 2026.
They each highlight one facet of the same question: as AI agents evolve from “assistants in a chat window” into “autonomous entities that can act, remember, and spend money,” how should we understand and govern this transformation? This report analyzes it around three pillars:
- Permission/Authority — What level of system access is granted to agents? Who authenticates, who audits, who can revoke? From MIT Media Lab’s attested delegation framework to OpenClaw’s “three lethal factors,” the boundaries of permission are being redrawn.
- Collaboration — How do agents discover one another, exchange information, and cooperate to complete tasks? From Google’s A2A protocol to the machine-native communication protocols that spontaneously emerged on Moltbook, collaboration paradigms are shifting from human-designed to self-organizing evolution.
- Employment — When AI becomes the employer and humans the executors, every assumption of traditional labor relations is shaken. RentAHuman.ai’s crypto-based task dispatching, the Phillips curve reproduced by EconAgent, and the complete legal vacuum together form a disturbing yet unavoidable picture.
Drawing on over ten recent studies, this report offers a panoramic and in-depth analysis of AI agents’ cognitive architectures, protocol standards, economic behaviors, security threats, and governance pathways.
2026-01-29
Related article: “Permissions, Collaboration, and Employment of AI Agents in Moltbook”
[This research report and Slides were co-produced with the assistance of Clawdbot + Claude Opus 4.5 models]
“Sovereign Agents: In-Depth Research on Clawdbot/OpenClaw” Slides 【Slidev source code】
Where is your data stored, and on whose hard drive? Whose instructions does your AI obey? Who controls your compute power?
For the past three years, we’ve accepted a tacit agreement: hand over personal data to cloud giants in exchange for convenient AI capabilities. GPT requires a subscription; Claude requires a subscription; Manus was fully closed-source after being acquired by Meta for $2 billion—each paradigm shift pushes users further away from controlling their own digital lives. In early 2026, an open-source project called Clawdbot tore up this unspoken contract.
Clawdbot (renamed Moltbot for trademark reasons, then later renamed OpenClaw) is the first open-source project to merge three major Agent capabilities—Deep Research, Computer Use, and Coding—into a single system. Its radical nature does not lie in the technology itself—the underlying LLM reasoning, tool-calling protocols, and local-first architecture are all already mature components—but in a core claim it proposes and actually implements: the Sovereign Agent. This claim is defined by three dimensions of autonomy:
- Data sovereignty — your files, chat history, and personal preferences always stay on your own hard drive, and never touch any third-party server;
- Compute sovereignty — you can choose to call cloud APIs, or run open-source models locally with Ollama, and even keep your Agent working on an offline airplane;
- Control sovereignty — every action of the Agent is entirely decided by you. No vendor-imposed limits behind the scenes, and no one else making “safety” judgments on your behalf—freedom and risk are both yours alone.
These three principles separate Clawdbot from all closed-source Agents, and also explain why it could explode in popularity within a day of release, surpass 70,000 GitHub stars in under a week, spawn hundreds of community plugins in 48 hours, and even trigger a spike in Mac Mini sales.
This report will dissect the phenomenon across six dimensions: its technical lineage and historical position; how the three types of sovereignty drive market breakout; the four-layer core architecture (multi-protocol gateway, Coding Agent engine, Markdown memory system, local execution and security sandbox); security risks and mitigation practices; a practical blueprint for building a sovereign Agent from scratch; and a forward-looking view on the return of personal computing and large models as the new operating system.
2026-01-25
[This article is adapted from a Zhihu answer. It was written the old-fashioned way, by hand, and is not AI-generated.]
For People and Models Alike, Context Is What Matters Most
Yesterday morning I was in a bad mood. I read two technical reports and felt like almost every well-known technical report had someone I knew on it, while I myself hadn’t produced anything.
Then I heard a part of Jiayi Weng’s interview. Roughly, he said: “I think the first profession to be replaced by AI is researcher. Next to be replaced is infra engineer like me. The hardest to replace is sales, because convincing someone to pay is not that easy for AI; it still needs human-to-human communication.”
That instantly cheered me up, because what we do is exactly communication and negotiation with people. This thing isn’t as hard as I imagined, and yet someone as senior as Jiayi Weng thinks it’s unlikely AI can do it well… I think one explanation is context.
2026-01-16
【The following content was整理ed by AI based on a recording, with no modifications made】
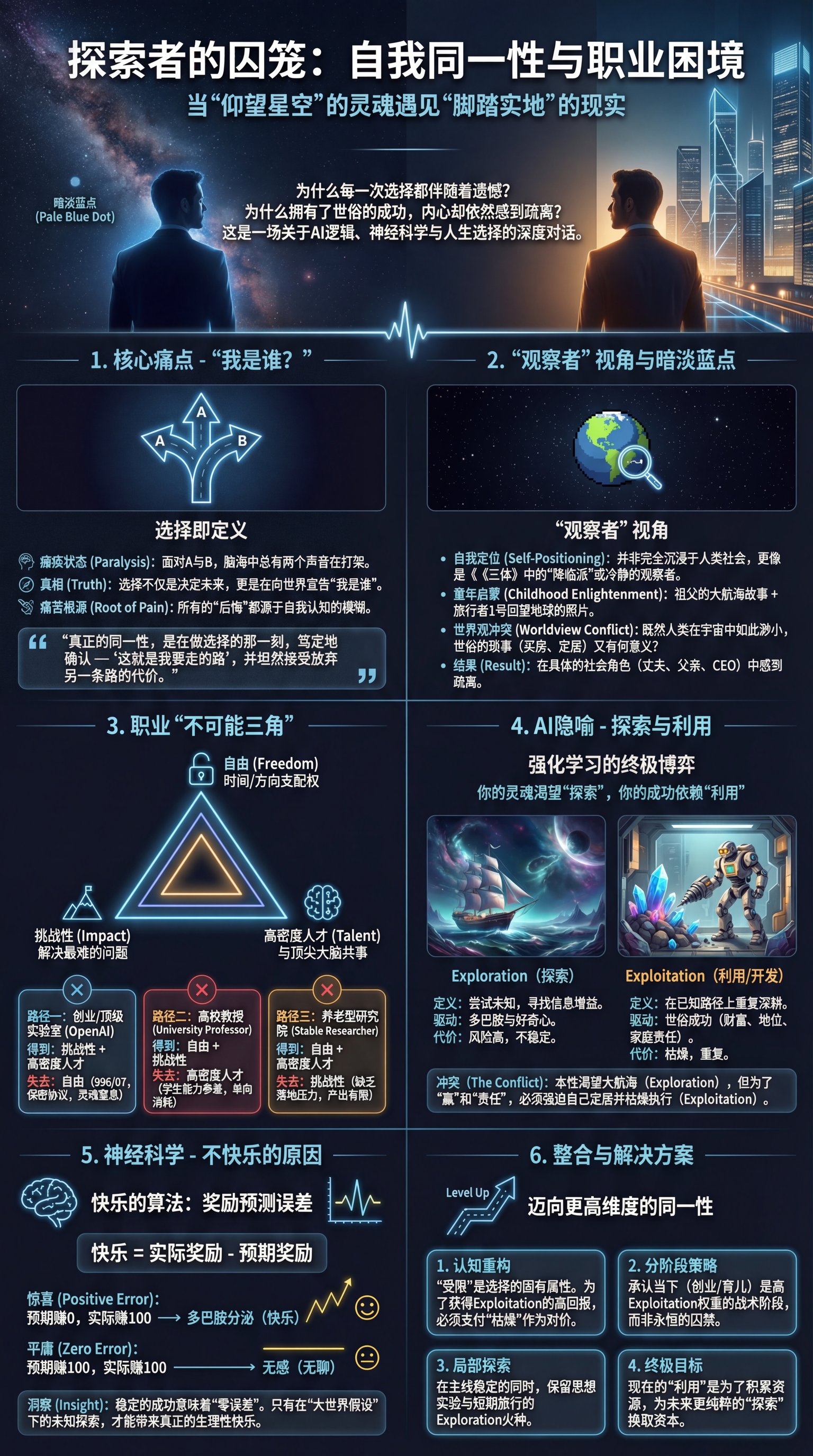
2026-01-11
This document provides a series of carefully designed AI Agent practical projects, covering three difficulty levels from easy to hard. These projects are intended to help students deeply understand the core technologies and design patterns of AI Agents, including tool use, multi-agent collaboration, long-term memory management, externalized learning, and other frontier topics. Each project includes clear experimental objectives, detailed descriptions of the experimental content, and specific acceptance criteria, ensuring that students can master the key skills needed to build advanced AI Agent systems through hands-on practice.
The projects are divided into three levels by difficulty. Students are advised to choose appropriate projects according to their own background and improve their abilities step by step.
Project Index
Difficulty: Easy
- Enhancing mathematical and logical reasoning ability using code generation tools
- Natural language interactive ERP Agent
- Werewolf Agent
Difficulty: Medium
- Personal photo search engine
- Intelligent video editing
- PPT generation Agent
- Book translation Agent
- Agent that collects information from multiple websites simultaneously
Difficulty: Hard
- A user memory that understands you better
- Agent that uses a computer while talking on the phone
- Computer operation Agent that gets more proficient the more you use it
- Agent that can create Agents
2026-01-04
I chatted with an AI for three hours and wrote two sets of reading notes (to test the AI’s capabilities, I deliberately did not make any edits to the AI-generated content).
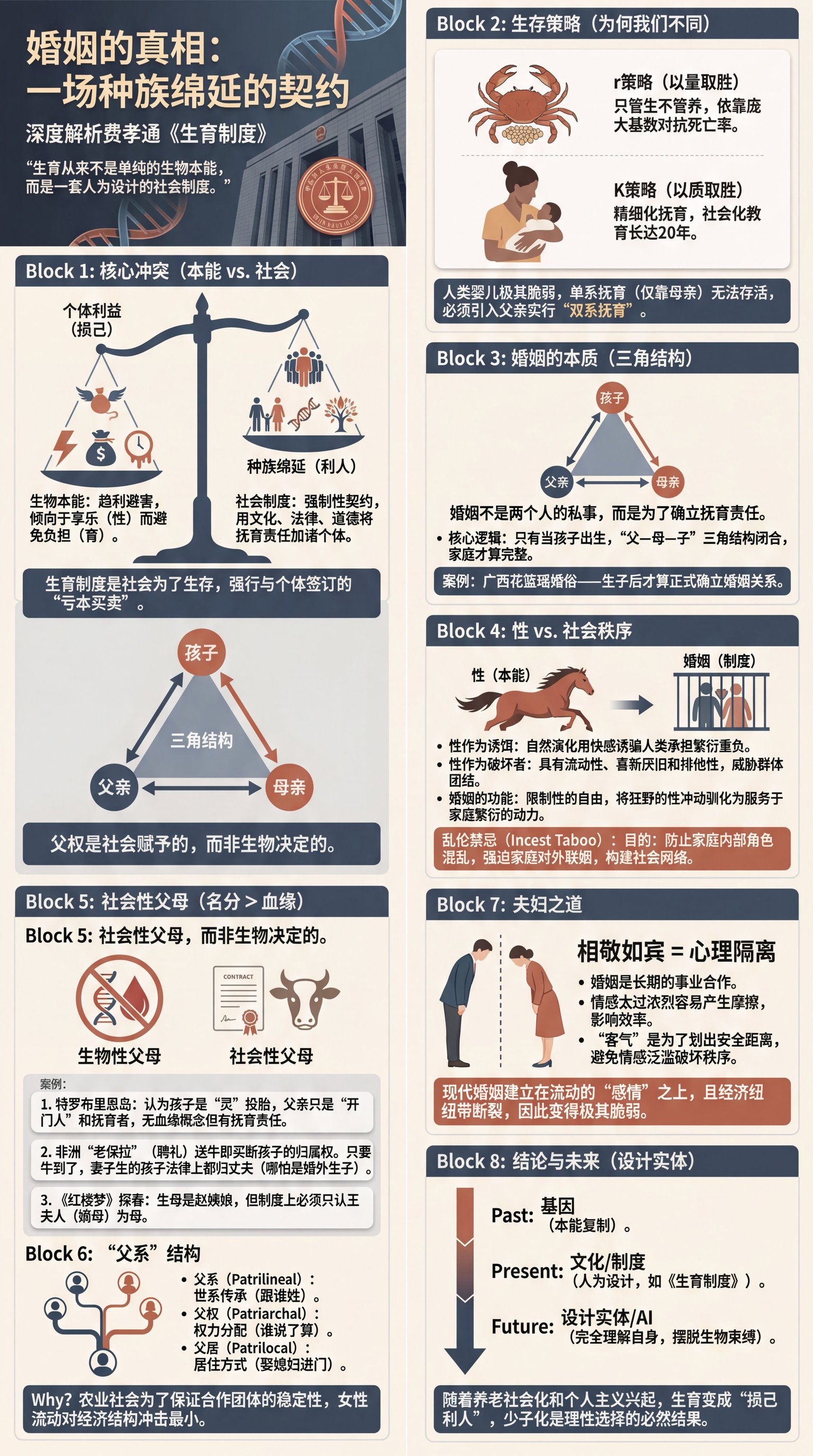
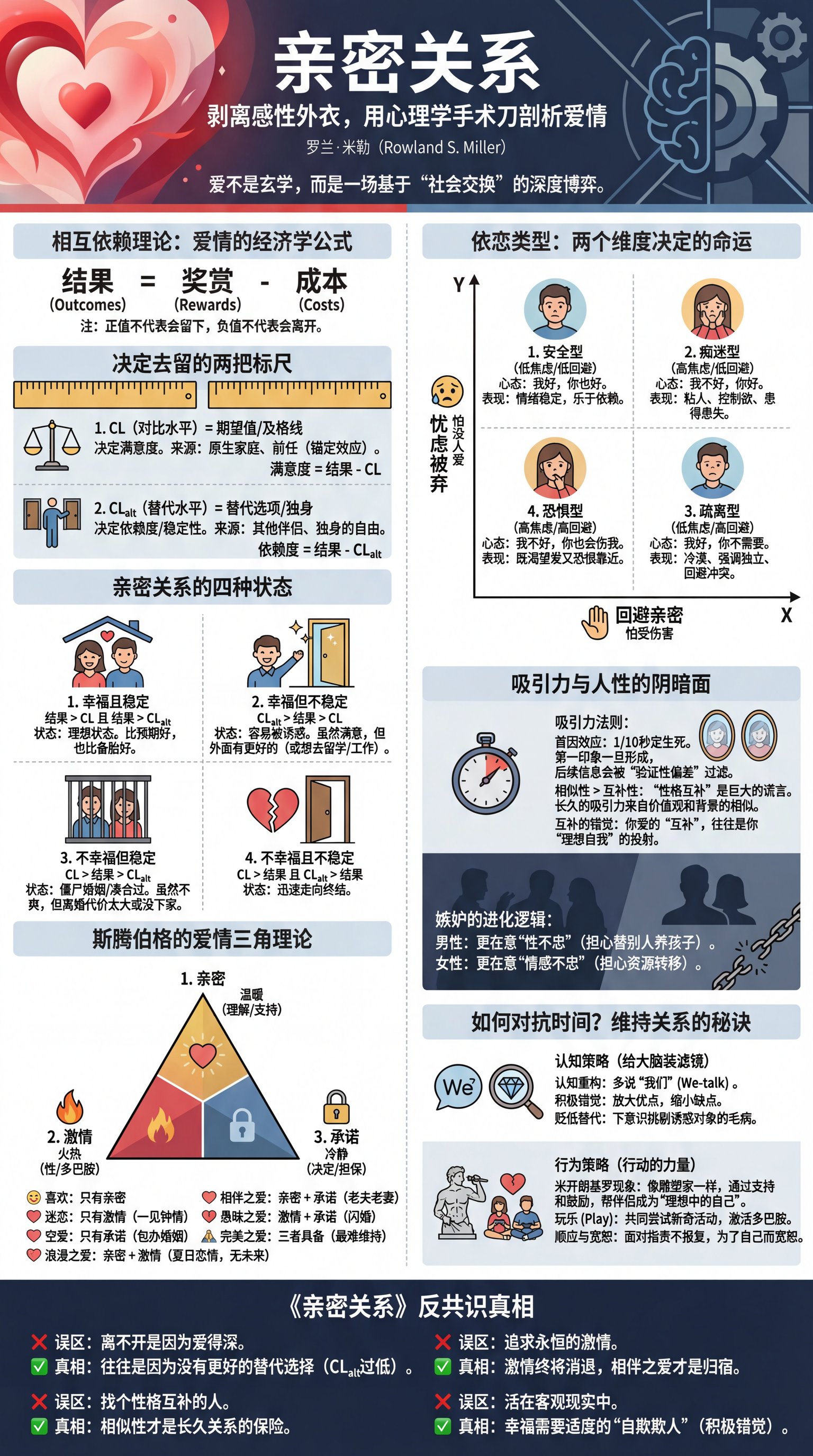
2025-12-21
This month, the Course Review Community encountered a storage performance issue that lasted nearly two weeks, causing slow service responses and degraded user experience. This post documents how the issue was discovered, investigated, and resolved, covering NFS performance, ZFS logs, Proxmox VE virtualization storage configuration, and more.
2025-12-20
(This article is organized from Anthropic team talks and in-depth discussions during AWS re:Invent 2025)
View Slides (HTML), Download PDF Version (note these slides are not official Anthropic material; I reconstructed them from photos and recordings)
Contents
Claude is already smart enough—intelligence is not the bottleneck, context is. Every organization has unique workflows, standards, and knowledge systems, and Claude does not inherently know any of these. This post compiles Anthropic’s best practices for Context Engineering, covering Skills, Agent SDK, MCP, evaluation systems and other core topics to help you build more efficient AI applications.
- 01 | Skills system - Let Claude master organization-specific knowledge
- 02 | Context Engineering framework - Four pillars for optimizing token utility
- 03 | Context Window & Context Rot - Understand context limits and degradation
- 04 | Tool design best practices - Elements of powerful tools
- 05 | Claude Agent SDK - A framework for production-ready agents
- 06 | Sub-agent configuration best practices - Automatic invocation and permissions
- 07 | MCP (Model Context Protocol) - A standardized protocol for tool integration
- 08 | Evaluations - Why evaluation matters and best practices
- 09 | Lessons from building Coding Agents - What we learned from Claude Code
- 10 | Ecosystem collaboration - How Prompts, MCP, Skills, and Subagents work together
2025-12-20
(This article is the invited talk I gave at the first Intelligent Agent Networks and Application Innovation Conference on December 20, 2025)
View Slides (HTML), Download PDF Version
Abstract
Today’s agent–human interaction is centered on text, but that deviates from natural human cognition. From first principles, the modality humans are best at for output is speech (speaking is three times faster than typing), and the modality humans are best at for input is vision. Vision is not text, but intuitive UI.
The first step is achieving real‑time voice interaction. The traditional serial VAD–ASR–LLM–TTS architecture suffers from having to wait for the user to finish speaking before it can start “thinking,” and it cannot output before the thinking is done. With an Interactive ReAct continuous‑thinking mechanism, the agent can listen, think, and speak at the same time: it starts thinking while the user is talking, and keeps deepening its reasoning while it’s speaking itself, making full use of all idle time gaps.
The second step is to expand the observation space and action space on top of real‑time voice. By extending the Observation Space (from voice input to Computer Use–style visual perception) and the Action Space (from voice output to UI generation and computer control), the agent can operate existing computer/phone GUIs while on a call, and generate dynamic UI to interact with the user. One implementation path for generative UI is generating front‑end code; Claude 4.5 Sonnet has already reached the threshold for this. Another path is generating images; Nano Banana Pro is also close to this threshold.
This is exactly the path used to realize Samantha in the movie Her. As an operating system, Samantha needs five core capabilities: real‑time voice conversation with the user, making phone calls and handling tasks on the user’s behalf, operating traditional computers and phones for the user, bridging data across the user’s existing devices and online services, having her own generative UI interface, and possessing powerful long‑term user memory for personalized proactive services.
2025-12-19
(This article is the invited talk I gave at AWS re:Invent 2025 Beijing Meetup)
Click here to view Slides (HTML), Download PDF version
Thanks to AWS for the invitation, which gave me the opportunity to attend AWS re:Invent 2025. During this trip to the US, I not only attended this world-class tech conference, but was also fortunate enough to have in-depth conversations with frontline practitioners from top Silicon Valley AI companies such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind. Most of the viewpoints were cross-validated by experts from different companies.
From the re:Invent venue in Las Vegas, to NeurIPS in San Diego, and then to AI companies in the Bay Area, more than ten days of intensive exchanges taught me a great deal. Mainly in the following aspects:
Practical experience of AI-assisted programming (Vibe Coding): An analysis of the differences in efficiency improvement in different scenarios—from 3–5x efficiency gains in startups, to why the effect is limited in big tech and research institutions.
Organization and resource allocation in foundation model companies: An analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of companies like Google, OpenAI, xAI, Anthropic, including compute resources, compensation structure, and the current state of collaboration between model teams and application teams.
A frontline perspective on Scaling Law: Frontline researchers generally believe that Scaling Law is far from over, which diverges from the public statements of top scientists such as Ilya Sutskever and Richard Sutton. Engineering approaches can address sampling efficiency and generalization issues, and there is still substantial room for improvement in foundation models.
Scientific methodology for application development: An introduction to the rubric-based evaluation systems that top AI application companies widely adopt.
Core techniques of Context Engineering: A discussion of three major techniques to cope with context rot: dynamic system prompts, dynamic loading of prompts (skills), sub-agents plus context summarization. Also, the design pattern of using the file system as the agent interaction bus.
Strategic choices for startups: Based on real-world constraints of resources and talent, an analysis of the areas startups should avoid (general benchmarks) and the directions they should focus on (vertical domains + context engineering).